Sports Performance
& Personalized Training
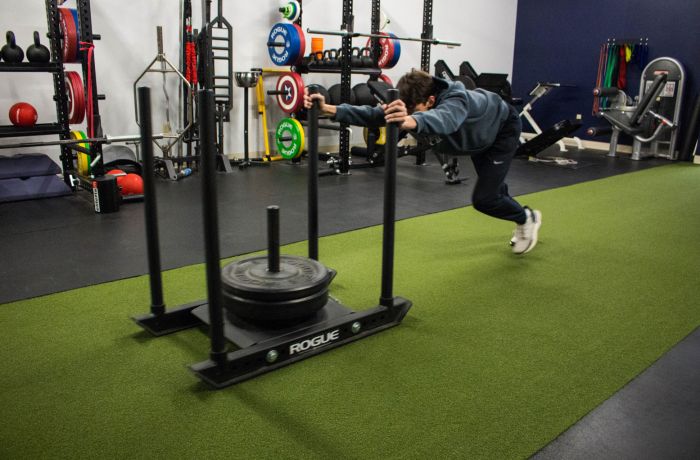
Located in Murrysville, PA, Gallagher Performance caters to individuals of all ages and athletes who are looking to take their health, fitness, or athletic abilities to the next level. We have quickly developed a reputation for having expertise in improving ALL aspects of athletic performance. Whether you’re looking to improve your speed, agility, strength, power, or sport-specific conditioning – Gallagher Performance will get you there.
Gallagher Performance is all about individualizing the training process. We offer programming that is focused on progressive development and acquisition of the necessary tools for success. You won’t find “whiteboard workouts” or “cookie-cutter programs” here! It’s one of our “secrets” to our success and why other local gyms or training centers can’t duplicate us. That’s because we understand each person responds differently to training due to a multitude of factors that must be accounted for.
Regardless of whether training occurs in a private or semi-private setting, clients are closely coached through the entirety of their program to maximize results. If your goal is to enhance your athletic performance, resolve chronic pain problems, or simply get in the best shape of your life, all of our clients begin with a comprehensive physical assessment. All the information gathered during your initial assessment is used to design an individualized training program. We take time to ensure that specialized attention is given to each program design.
Gallagher Performance is all about individualizing the training process. We offer programming that is focused on progressive development and acquisition of the necessary tools for success. You won’t find “whiteboard workouts” or “cookie-cutter programs” here! It’s one of our “secrets” to our success and why other local gyms or training centers can’t duplicate us. That’s because we understand each person responds differently to training due to a multitude of factors that must be accounted for.
Regardless of whether training occurs in a private or semi-private setting, clients are closely coached through the entirety of their program to maximize results. If your goal is to enhance your athletic performance, resolve chronic pain problems, or simply get in the best shape of your life, all of our clients begin with a comprehensive physical assessment. All the information gathered during your initial assessment is used to design an individualized training program. We take time to ensure that specialized attention is given to each program design.
Gallagher Performance is committed to providing the best for all of our clients.
Why Gallagher Performance?
Initial 1-on-1 Assessments
Custom & Individualized Program Design
Supervised Training Sessions
Positive & Supportive Atmosphere
Nutritional Approach

Our nutritional approach at Gallagher Performance is focused on sustainability through client care and success. At Gallagher Performance our programs are developed around practical application and science, absent of cookie-cutter planning and gimmicks. All nutrition programs are purely customized and special attention is directed towards the client’s specific needs. If the program is not sustainable, it will not be successful. And nothing is more important to the staff at Gallagher Performance than your success. Sustainable actions produce optimum results.

TRAINING & NUTRITIONAL SERVICES OFFERED:
- Sports Performance & Athletic Development Programs
- Strength Programs
- Corrective Exercise Programs
- Body Building & Physique Competitor Programs
- Personal Training Programs
- Nutritional Consultations & Programs
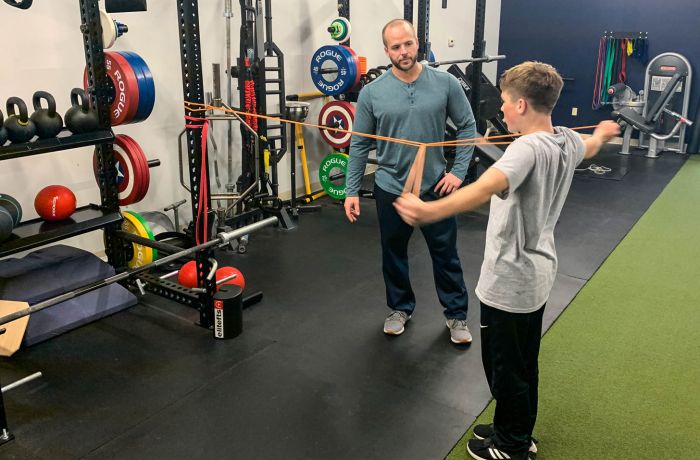
Why Athletic Development Matters
When it comes to athletes, critical developmental stages begin at an early age. As children mature, they progress through these important developmental stages during their growth and maturation process. If long-term athletic development is of any importance to the coach, parent, or athlete, specific aspects of athletic development must be addressed at appropriate time periods, otherwise the chances of the athlete reaching elite status is reduced.
The model used at Gallagher Performance began with a review of research and methods utilized in child and athletic development around the world. Through the review of current and past training methods used with elite athletes, it was concluded that to truly address athlete development, a new way of looking at how to properly structure “Strength and Conditioning” programs must be considered.
The reason is because early specialization in sport is becoming increasingly more common amongst children in the United States, and it’s not working. The rationale behind such a decision typically being if a child plays one sport, year round, they will be more advanced than their peers, more likely to be the ‘star’, get recruited, and/or possibly go on to make millions.
The model used at Gallagher Performance began with a review of research and methods utilized in child and athletic development around the world. Through the review of current and past training methods used with elite athletes, it was concluded that to truly address athlete development, a new way of looking at how to properly structure “Strength and Conditioning” programs must be considered.
The reason is because early specialization in sport is becoming increasingly more common amongst children in the United States, and it’s not working. The rationale behind such a decision typically being if a child plays one sport, year round, they will be more advanced than their peers, more likely to be the ‘star’, get recruited, and/or possibly go on to make millions.
Recent research from UCLA reveals that early specialization in sport has very poor connection with young athletes achieving elite status. A survey of almost 300 NCAA Division I athletes found that 88% played two or three sports as children and 70% did not specialize in one sport until after the age of 12. These findings were already understood in former East Germany and USSR within their youth development programs.
Studies in former East Germany and USSR found that children who went through an early specialization program did have more immediate improvement in their performances. But these children also had their best performances between the ages of 15-16, had greater inconsistencies, many quit or ‘burnt out’ by the age 18, and they had greater rate of injuries because of forced adaptation compared to children who played multiple sports and specialized later in life.
Long-term athletic development is a process that occurs over many years. This is not an “8 week program”. Rather, it starts at an early age and continues on into adulthood. Long-term athletic development is about progressive development and must be approached accordingly. It is not simply a linear process, but is one that must be highly individualized to assist the athlete in reaching their full potential.
The greatest challenge to coaches, parents, and athletes is the understanding of how difficult this process is. Young athletes are continually dealing with massive changes in physical attributes, brain function, and sport skill acquisition. These all must be managed simultaneously while stressing the concepts of hard work in a positive environment.
Long-term athletic development is a process that occurs over many years. This is not an “8 week program”. Rather, it starts at an early age and continues on into adulthood. Long-term athletic development is about progressive development and must be approached accordingly. It is not simply a linear process, but is one that must be highly individualized to assist the athlete in reaching their full potential.
The greatest challenge to coaches, parents, and athletes is the understanding of how difficult this process is. Young athletes are continually dealing with massive changes in physical attributes, brain function, and sport skill acquisition. These all must be managed simultaneously while stressing the concepts of hard work in a positive environment.
TPI Golf Therapy
Gallagher Performance offers individualized, golf-specific rehabilitation to performance programs. As a Titleist Performance Institute (TPI) Certified Medical Level 2 Professional, Dr. Gallagher will take you through a comprehensive physical screen to determine functional limitations in your body. This 16-step process serves to identify your ideal body swing connection, enabling golfers to find new efficiency in their game while avoiding injury inducing swing mechanics.
When it comes to the rehabilitation of golf-specific injuries, the information gathered from your TPI physical screen is combined with further movement diagnostic testing to pinpoint the exact cause of your pain and physical limitations. These become the keys to designing the early stages of your golf-specific rehabilitation program.
Gallagher Performance's Golf Rehabilitation & Performance offers:
- Titleist Performance Institute body swing connection physical screen
- Complete golf-specific physical performance testing
- Customized program designed to the player’s needs
- Increased coordination, stability, power, and club head speed
As we progress from rehabilitation to return-to-play, our focus must shift to performance. We dive in strength, power, and other physical indicators that translate into more club head speed, greater consistency in your game, and increased resilience of your body.
Whether you are looking to play pain free golf or lower your handicap, the TPI professional at Gallagher Performance is able to develop a program designed to reach your goals and elevate your golf game.